Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions
Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Enthalpy of Atomization, Electron Gain Enthalpy, Enthalpy of Formation, Standard Enthalpy of Formation, Enthalpy of Neutralization, Bond Enthalpy, Lattice Enthalpy, Resonance Energy and, Enthalpy of Fusion
Important Questions on Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions
From the data of following bond energies:
Calculate the enthalpy of the following reaction in .
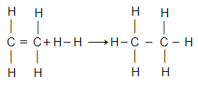
Given that bond energies of respectively and for , bond enthalpy of is:
For which one of the following equations is equal to for the product?
The values of heat of formation of are –298.2 kJ and –98.2 kJ. The enthalpy change of the reaction
will be
The absolute enthalpy of neutralisation of the reaction:
will be:
[Consider the actual value instead of magnitude].
Equal volumes of molar hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid are neutralized by dilute NaOH solution and x kcal and y kcal of heat are liberated respectively. Which of the following is true?
When litres of a gas mixture of methane and propane is perfectly combusted at and , of oxygen at the same temperature and pressure is consumed. The amount of heat released from this combustion in is :
For which one of the following equation is equal to for the product ?
During the phase change of a substance enthalpy is changed.
Units of Enthalpy of Transition
Explain enthalpy of transition?
In Kirchhoff's equation, the term is used instead of at constant volume.
Kirchhoff's equation at constant volume is :
The variation of with temperature is expressed by Kirchoff's equation.
Temperature affects the enthalpy change of a reaction.
Write the Kirchhoff's equation at constant volume and at constant pressure.
Specific heat capacity is not the parameter that is used to relate the enthalpy of a reaction and temperature.
Describe the effect of temperature on enthalpy of reaction.
What happens to the enthalpy of the system if its temperature increases?
Give the Kirchhoff's equation at constant volume.
